SQL Working With Dates
The most difficult part when working with dates is to be sure that the format of the date you are trying to insert, matches the format of the date column in the database.
SQL Date Data Types
MySQL comes with the following data types for storing a date or a date/time value in the database:
- DATE - format YYYY-MM-DD
- DATETIME - format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS
- TIMESTAMP - format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS
- YEAR - format YYYY or YY
- DATE - format YYYY-MM-DD
- DATETIME - format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS
- SMALLDATETIME - format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MI:SS
- TIMESTAMP - format: a unique number
SQL Working with Dates
Look at the Product table:
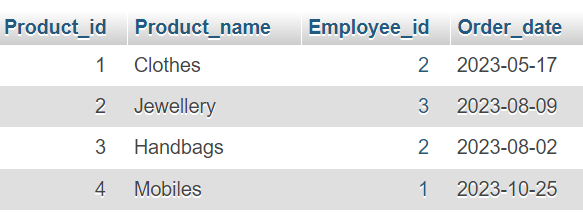
Now we want to select the records with an Order_date of "2023-05-17" from the table above.
We use the following SELECT statement:
Example
SELECT * FROM
products WHERE Order_date = '2023-05-17';
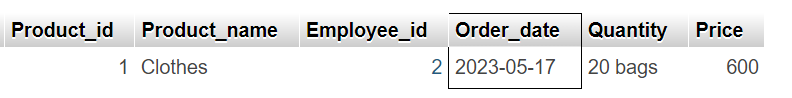
Now, assume that the "Orders" table looks like this (notice the added time-component in the "OrderDate" column):

If we use the same SELECT statement as above:
we will get no result! This is because the query is looking only for dates with no time portion.
