The SQL HAVING Clause
The HAVING clause is use because the WHERE keyword cannot be used with aggregate functions.
Syntax
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column_name(s) HAVING condition ORDER BY column_name(s) ;
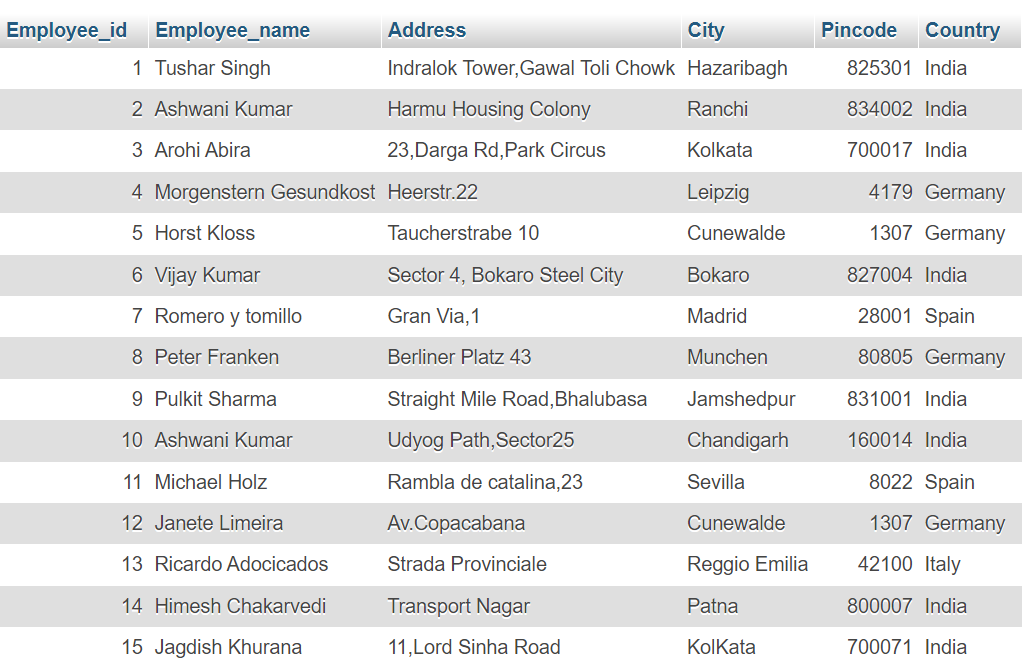
Demo Employee table
This employee table is used for examples:
SQL HAVING Examples
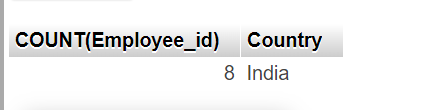
The following SQL statement lists the number of employee in each country. Only include countries with more than 5 employee:
Example
SELECT COUNT(Employee_id), Country FROM employee GROUP BY Country HAVING COUNT(Employee_id) > 5;You can click on above box to edit the code and run again.
Output
The following SQL statement lists the number of employee in each country, sorted high to low (Only include countries with more than 2 cemployee):
Example
SELECT COUNT(Employee_id), Country FROM employee GROUP BY Country HAVING COUNT(Employee_id) > 2 ORDER BY COUNT(employee_id) DESC ;You can click on above box to edit the code and run again.
Output

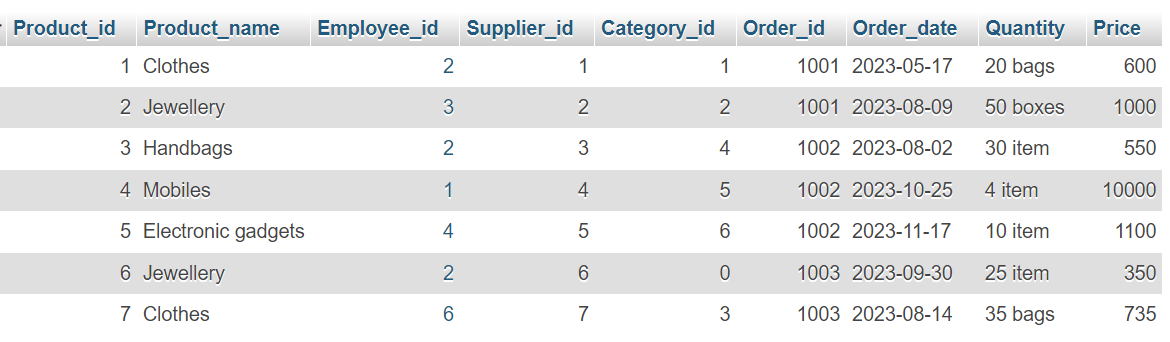
Demo Products table
This product table is used in examples:
More HAVING Examples
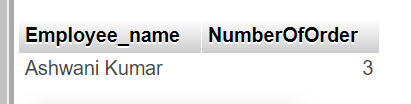
The following SQL statement lists the employee that have registered more than 2 orders: