CSS Layout - The z-index Property
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a style sheet language used for describing the look and formatting of a document written in HTML or XML. CSS includes various properties that control the layout and presentation of elements on a web page.
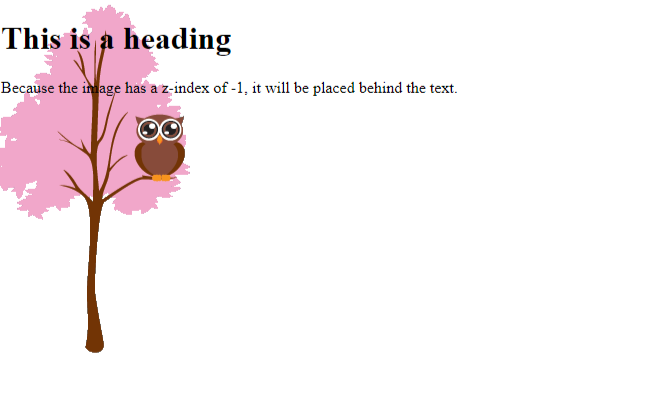
The z-index property is a crucial aspect of CSS layout and is used to control the stacking order of positioned elements. When elements overlap on a web page, the z-index property determines which element appears in front of the others.
Another z-index Example
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Z Index</title>
<style>
.container {
position: relative;
}
.box1-box {
position: relative;
z-index: 1;
border: 2px solid black;
height: 100px;
margin: 40px;
background-color: aqua;
}
.box2-box {
position: absolute;
z-index: 3;
background-color: rosybrown;
height: 60px;
width: 70%;
left: 250px;
top: 50px;
border: 2px solid;
}
.box3-box {
position: absolute;
color: wheat;
z-index: 2;
background-color: rebeccapurple;
width: 45%;
left: 270px;
top: 15px;
height: 100px;
border: 2px solid;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS z-index</h1>
<div class="container">
<div class="box1-box">Box 1 (z-index: 1)</div>
<div class="box2-box">Box 2 (z-index: 3)</div>
<div class="box3-box">Box 3 (z-index: 2)</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
You can click on above box to edit the code and run again.Output
CSS Z Index
CSS z-index
Box 1 (z-index: 1)
Box 2 (z-index: 3)
Box 3 (z-index: 2)